Introduction
April is recognized globally as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) month. According to the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, approximately 10 to 15 percent of the global population experiences IBS. It is more common in women and often develops before age 40.
While not fatal, IBS is a persistent condition without a recognized cure. Understanding the types of IBS, the symptoms, and how lifestyle choices affect it are essential to the prevention and management of this condition.
What is IBS?
IBS is a gastrointestinal disorder that is characterized by abdominal discomfort or pain associated with altered bowel movements. There are four main subtypes of IBS based on the predominant bowel symptom: Diarrhea (IBS-D), constipation (IBS-C), mixed (IBS-M), and unspecified (IBS-U). The subtype determines the appropriate treatment approach, but all types share common symptoms and triggers.
Causes and Symptoms of IBS
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hypersensitivity of the nerves in the gut, issues with how the gut and brain communicate, and factors like diet, stress, and gut microbiome changes.
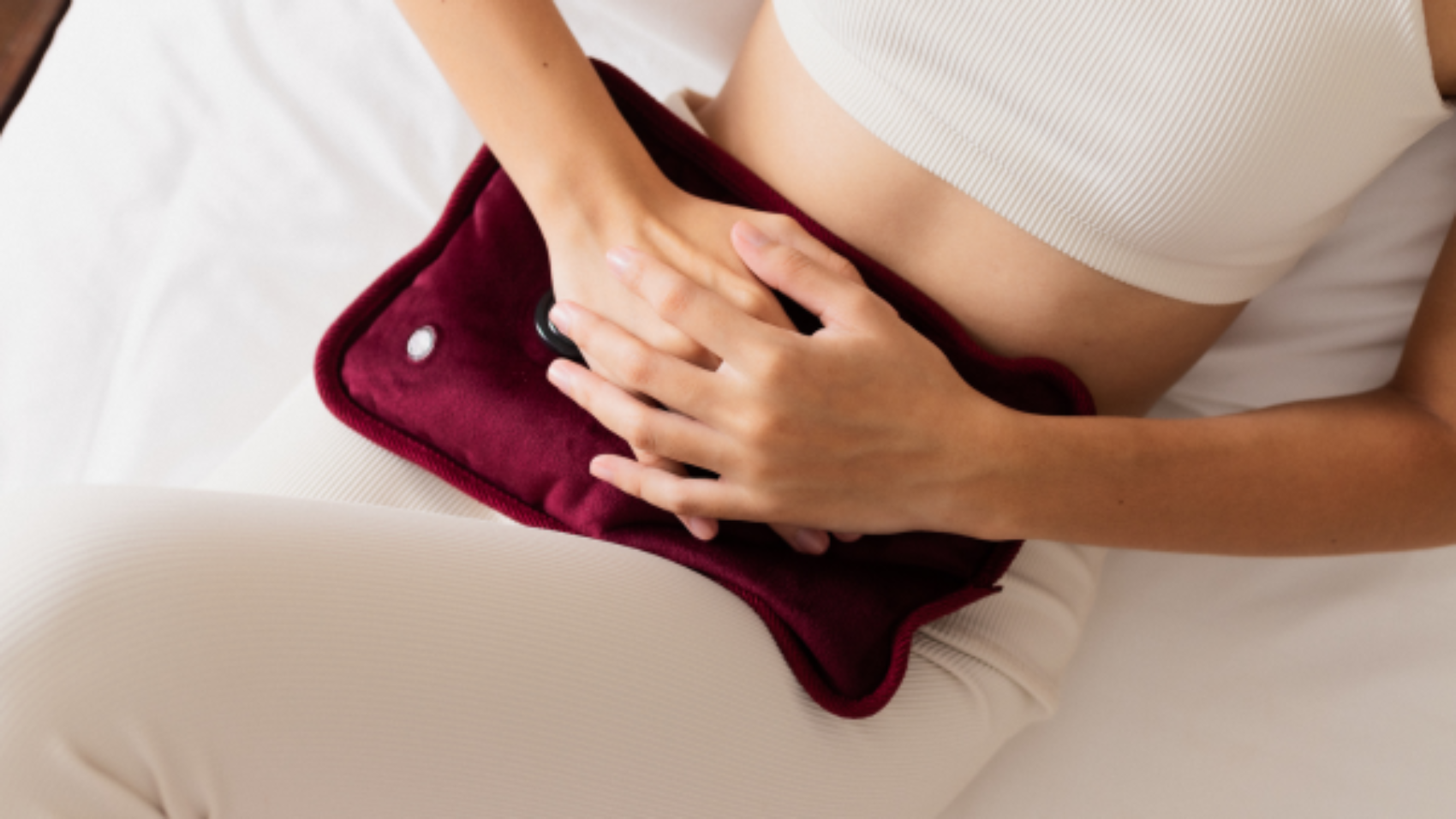
It is considered a chronic condition that affects the digestive system, causing symptoms like stomach cramps, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. However, it does not cause permanent damage to the digestive tract or increase the risk of more serious conditions like colon cancer. The symptoms tend to come and go over time and can be managed through diet, lifestyle changes, and medications.
Common Triggers of IBS
The specific triggers for IBS can vary from person to person, so keeping a food and symptom diary helps to identify individual triggers. Working closely with a doctor or dietitian can also help manage IBS by identifying and avoiding personal triggers, but the following are a few of the more common triggers:
- Dietary triggers. Insoluble fiber-rich foods like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. This includes gluten-containing foods like wheat, rye, and barley. Dairy products, especially for those with lactose intolerances, fried and fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated drinks also make the list. Foods high in fructose and sorbitol, may also be triggering.
- Stress and anxiety. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate IBS symptoms and trigger flare-ups.
- Medications. Certain medications like antibiotics, antidepressants, and cough syrups containing sorbitol can trigger IBS symptoms.
- Hormonal changes. For women, hormonal changes around menstruation can trigger IBS symptoms.
- Infections and other gastrointestinal conditions. Bacterial infections, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and other GI disorders can contribute to the development of IBS.
Additionally, many of the food triggers identified with IBS are common with food intolerances. For more information, check out our blog on Food Intolerances.
How Lifestyle Affects IBS Symptoms
The lack of defined cause, uncomfortable symptoms, and the multitude of common triggers may seem discouraging. But there are lifestyle choices that can help manage IBS symptoms:
- Dietary choices. Avoid foods and beverages that are known to be common IBS triggers. Follow a low-FODMAP diet by avoiding foods high in fermentable carbohydrates like wheat, onions, fruits, and dairy products.
- Exercise. Regular moderate exercise like walking can improve bowel function and reduce stress. Yoga has been shown to be as effective as a low-FODMAP diet in reducing IBS symptoms.
- Stress management. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, mindfulness, and deep breathing to help manage stress and anxiety, which can trigger IBS.
- Sleep. Aim for adequate, quality sleep as poor sleep can exacerbate IBS symptoms.
The key is to experiment with different remedies and lifestyle changes and find what works best to manage your individual IBS symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare provider can also help develop an effective treatment plan.
Conclusion
In summary, IBS is a chronic, often lifelong condition that causes uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms but does not lead to more serious health problems. While IBS lacks a cure, awareness and proactive lifestyle choices can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.